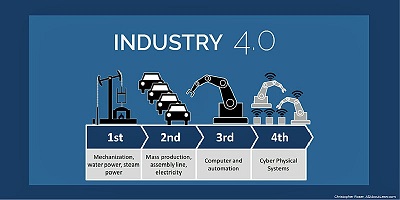
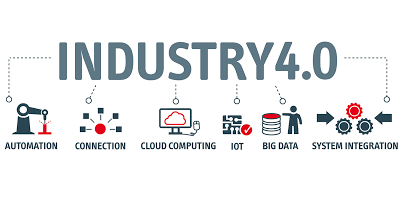
Industry 4.0 is a name given to the current trend of automation and data exchange in manufacturing technologies. It includes cyber-physical systems, the Internet of things, cloud computing and cognitive computing. Industry 4.0 is commonly referred to as the fourth industrial revolution.
Businesses can create huge volumes of data without realising it and this data can be a source of untapped value for business improvement and growth. In an Industry 4.0 context, the collection and comprehensive evaluation of data from many different sources—production equipment and systems as well as enterprise- and customer-management systems—will become standard to support real-time decision making.
The deployment of cyber-physical systems in production systems gives birth to the "smart factory." Smart factory products, resources and processes are characterized by cyber-physical systems; providing significant real-time quality, time, resource, and cost advantages in comparison with classic production systems.
The deployment of cyber-physical systems in production systems gives birth to the "smart factory." Smart factory products, resources and processes are characterized by cyber-physical systems; providing significant real-time quality, time, resource, and cost advantages in comparison with classic production systems.
Smart manufacturing and the Smart Factory is a broad category of manufacturing with the goal of optimizing the manufacturing process. Smart manufacturing is the process that employs computer controls, modeling, big data and other automation to improve manufacturing efficiencies. Smart manufacturing aims to take advantage of advanced information and manufacturing technologies to enable flexibility in physical processes to address a dynamic and global market.
Our MES (Manufacturing Execution System) and Asset Management Solution will put you on the path of Smart manufacturing and it will be first step towards the Smart Factory.
IoT is short for Internet of Things. The Internet of Things refers to the ever-growing network of physical objects that feature an IP address for internet connectivity, and the communication that occurs between these objects and other internet-enabled devices and systems. Your Wi-fi doorbell, or smart refrigerator are everyday examples of IoT devices.
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is a subset of IoT, aimed specifically at industrial applications. IIoT is about connecting machines to other machines/data management and the optimization and productivity that is possible to make “smart factories.”
Machines, devices, sensors and people that connect and communicate with one another. Interoperability is in essence what happens when we bring the above elements together. It is the connection of cyber-physical systems, humans and smart factories communicating with each other through the IoT. In doing so, manufacturing partners can effectively share information, error-free. Consider that no single company can dictate all its partners use the same software or standards for how the information is represented. Interoperability enables error-free transmission and translation.